The Concept of Transportation of Materials in Living Things
Explain the concept of transportation of materials in living things
Unicellular organisms (for example amoeba), nutrients (for example oxygen and food) and waste products (for example carbon dioxide) can simply diffuse into or out of the cells from the surroundings. But in multi cellular organisms (for example humans and trees), many cells are very far away from the body surface, hence a transport system is required for the exchange of materials.
Organisms require transport systems so as to carry out various life processes. These life processes include nutrition, respiration, excretion, growth and development, movement,reproduction and coordination. For these life processes to take place, transport of materials is inevitable. Materials are transported either from environment into the organisms or from one part of an organism to another, and can also be transported from an organism into the environment.
For example, during nutrition organisms take in food substances that they need to produce energy, grow and carry out other life processes. These food substances must be taken in from the environment. The same case applies to reproduction which requires the movement of gametes(sex cells) from the sex organs to the area where fertilization occurs. Therefore, transport is very important for the survival and existence of living things.
The Importance of Transportation of Material in Living Things
Outline the importance of materials in living things
Transport of materials is very important for the survival and development of living organisms. If transportation never existed, then no life on earth could be possible. The following is an outline of the importance of transport of materials in living things:
- It facilitates the removal of waste materials from the organism’s body, the excess of which could harm an organism.
- It ensures that essential materials like oxygen, nutrients, water, hormones and mineral salts are supplied to the cells and tissues as required.
- It enables essential substances to move from one part of the body to another. For example, food manufactured by photosynthesis in plant leaves is transported from leaves to other organs of the plant for use or storage.
Diffusion, Osmosis and Mass- flow
The Meaning of Osmosis, Diffusion and Mass- Flow
Explain the meaning of osmosis, diffusion and mass- flow
Life processes in organisms take place at the cell level. Therefore, it is necessary for substances to move in and out of the cells. There are two ways through which substances can move across the membrane. Materials in living organisms move by diffusion, osmosis and mass flow.
Diffusion
This is the movement of materials from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until equilibrium of two sides is maintained. Diffusion can also be defined as the movement of ions or molecules from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration, without involving any permeable membrane. A difference in concentration of a substance between two regions is known as concentration gradient.
Diagram showing diffusion
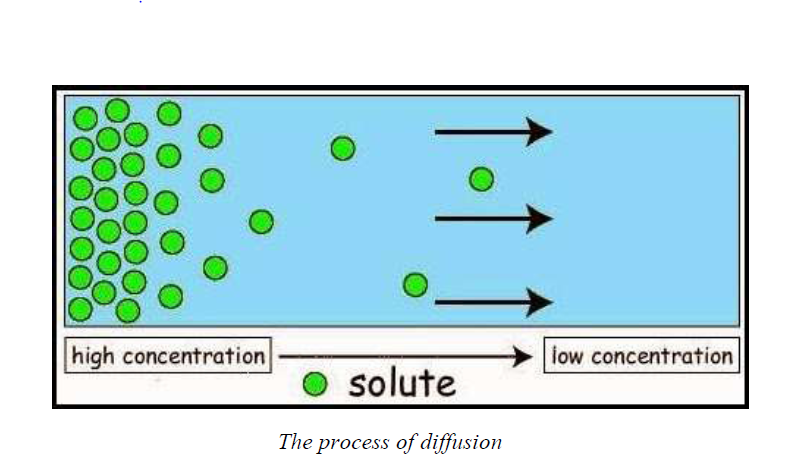
Materials are transported in the body system of living things from the area where they are abundant to areas where they are less abundant, and this process or mechanism of transportation in these animals is termed as diffusion. Diffusion occurs in exchange of gases like oxygen or carbon dioxide during respiration in animals and plants. Also, diffusion takes place during distribution of nutrients and digested foods in living organisms.
Osmosis
This is the movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. A partially-permeable membrane is a membrane that allows small particles such as water molecules to pass through it, but not larger particles such as sugar molecules and ions from salts. Examples of semi-permeable membranes are cell membranes and a pig’s bladder. These membranes allow transportation of water through them. In spite of the fact that they allow transportation of water through them, they do not permit the passage of sugar or salt molecules because they are solutes. Osmosis occurs when water moves down its concentration gradient across the semi-permeable membrane.
Therefore, for osmosis to take place there must be:
- two solutions with different concentrations; and
- a partially permeable membrane to separate them.
A dilute solution has a high water concentration, while a concentrated solution has a low water concentration. For example, when salt is dissolved in water:
- A little dissolved salt produces a dilute solution with a high water concentration
- A lot of dissolved salt produces a concentrated solution with a low water concentration.
Diagram of osmosis

Mass flow
Diffusion and osmosis occurs very slowly and cover short distances. In animals and plants, materials are usually transported a long distance and in large quantities. For example, food nutrients from the small intestine have to be moved to cells in the extremities such as toes and fingers, where the nutrient materials have to be transported a long distance. Therefore, an efficient and fast mechanism is required to facilitate this movement. That is when mass flow comes in.
Mass flow is the movement of materials in large quantities and across a long distance in the body of an organism due to differences in pressure between the two regions. Materials in higher plants and animals are moved by the process of mass flow. For example, the manufactured food in plant leaves has to be moved to all plant parts, for use or storage, by mass flow.
Experiments to Demonstrate the Process of Diffusion, Osmosis and Mass Flow
Carryout experiments to demonstrate the process of diffusion, osmosis and mass flow
Demonstration of the process of diffusion
Take a bottle of perfume and move to one corner of the classroom. Open a bottle and observe what happens. The result is, after a few seconds, the whole classroom is filled with a smell of the perfume. This means that the molecules of the perfume moves from the region of higher concentration (the bottle) to a region of lower concentration (air). That is why the smell is felt by a person standing several meters away from the source of the perfume.
Some important processes that involve diffusion are:
- Gaseous exchange in the lungs of animals and in the leaves of plants
- Absorption of digested food in the ileum the process of diffusion
- Removal of west materials from cells
- Absorption of nutrients and oxygen into cells
Demonstration of the process of osmosis
Procedure
Peel a potato and cut it as shown in the diagram below. Then fill the depression with brine(concentrated solution of sodium chloride). Leave the set up until the next day and observe what happens to the level of brine in the potato.
Result
In the following day, you will find that the level of brine will have risen as shown. This means that water has moved from the potato to the brine solution causing the brine level to rise up. The water has moved from a region of high water concentration (the potato) through the cell membranes of the potato cells (partially permeable membrane) to the region of low water concentration (the brine).

The Differences between Diffusion, Osmosis and Mass Flow
Outline the differences between diffusion, osmosis and mass flow
Differences between diffusion and osmosis
Diffusion
|
Osmosis
|
It is the movement of all types of substances from the area of their higher concentration to the area of their lower concentration
|
It is the movement of only solvent or water from the area of their higher concentration to the area of their lower concentration through a partially permeable membrane
|
Diffusion can operate in any medium
|
Osmosis operates only in a liquid medium
|
Diffusion is applicable to all types of substances (soilds, liquids and gases)
|
It is applicable only to solvent part of a solution
|
It does not require any semi-permeable membrane
|
A semi-permeable membrane is a must for operation of osmosis
|
It is purely dependent upon the free energy of the diffusing substance
|
Osmosis is dependent upon the degree of reduction of free energy of one solvent over that of another
|
It helps in equalizing the concentration of the diffusing substance throughout the available space
|
It does not equalize the concentration of solvent on the two sides of the system
|
Turgor pressure or hydrostatic pressure does not normally operate in diffusion
|
Osmosis is opposed by turgor or hydrostatic pressure of system
|
It is not influenced by solute potential
|
Osmosis is dependent upon the solute potential
|
Diffusion of a substance is mostly dependent of the presence of other substances
|
It is dependent upon the number of particles of other substances dissolved in a liquid
|
Factors like water potential, solute potential and pressure potential do not affect diffusion
|
Factors like water potential, solute potential and pressure potential affect osmosis in a living system
|
The Roles of Diffusion, Osmosis and Mass Flow in Movement of Materials in Living Organisms
Explain the roles of diffusion, osmosis and mass flow in movement of materials in living organisms
Materials are transported in the body system of living things from the area where they are abundant to areas where they are less abundant, and this process or mechanism of transportation in these animals is termed as diffusion. Diffusion occurs in exchange of gases like oxygen or carbon dioxide during respiration in animals and plants. Also, diffusion takes place during distribution of nutrients and digested foods in living organisms.
- Through the process of osmosis, nutrients get transported to cells and waste materials get moved out of them.
- The pressure within and outside each cell is maintained by osmosis as this process ensures a balance of fluid volume on both sides of the cell wall. If fluid volume within a cell is more than the fluid volume outside it, such pressure could lead the cell to become turgid and explode. On the contrary, if fluid volume outside the cell is more than the fluid volume within, such pressure could lead the cell to cave in. Both cases would be detrimental to normal and healthy cellular function.
- It is via osmosis only that roots of plants are able to absorb moisture from the soil and transport it upwards, towards the leaves to carry out photosynthesis. Plants wouldn't exist without osmosis; and without plants, no other life could exist as they are a vital link of the entire food chain of the planet.
- Without osmosis, it would be impossible for our bodies to separate and expel toxic wastes and keep the bloodstream free from impurities. The process of blood purification is carried out by the kidneys which isolate the impurities in the form of urine.
- Therefore, the role of osmosis is to fold: it helps maintain a stable internal environment in a living organism by keeping the pressure of intercellular and intracellular fluids balanced. It also allows the absorption of nutrients and expulsion of waste from various bodily organs on the cellular level. These are two of the most essential functions that a living organism cannot do without.
Transport of Materials in Mammals, the Structure of the Mammalian Heart




The Blood


Blood Groups and Blood Transfusion

Blood Circulation
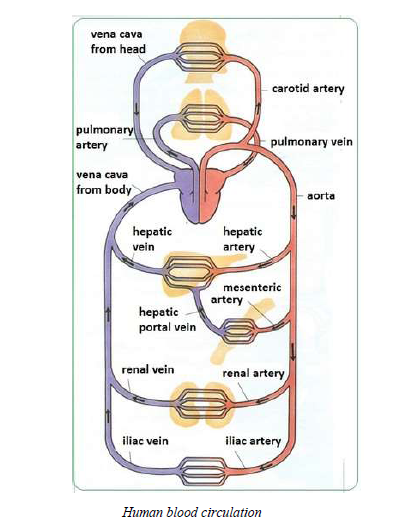
The Lymphatics System

Transport of Material in Plants in Plants, the Vascular System






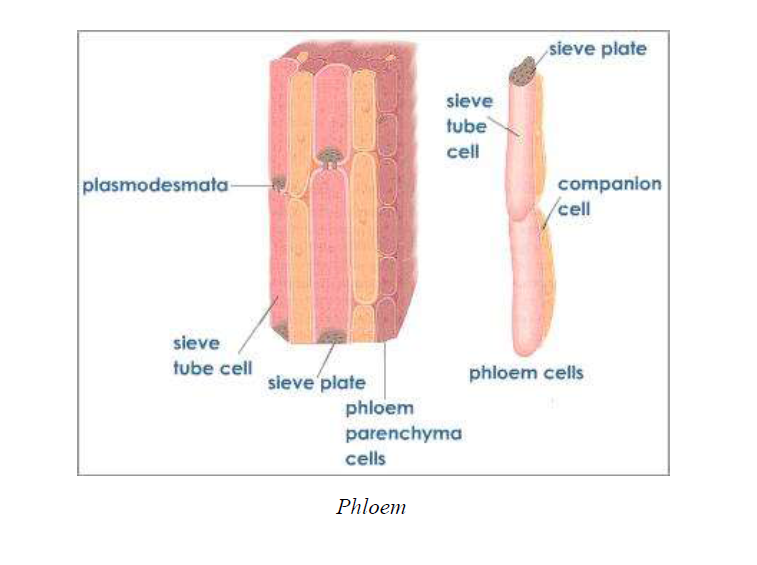
Absorption and Movement of Water and Mineral Salts in Plants

...
[
[



No comments:
Post a Comment